Focus Stacking
A technique that combines multiple images taken at different focus distances to produce a final image with a greater depth of field.
| Input Image Sequences | Result |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Codes available at: https://github.com/bznick98/Focus_Stacking |
What is Focus Stacking?
Focus stacking is a technique used in photography to increase the depth of field in an image by combining multiple images taken at different focus distances into a single image with greater sharpness and clarity from foreground to background. The process involves taking multiple shots of the same scene, each with a different focus distance, and then combining them into one single clear image. (Detailed Photography Guide)
How to achieve Focus Stacking?
I researched several methods including findning maximum laplacian of gaussian (LoG) and using laplacian pyramid decomposition. Among of all methods, I find fusing images using laplacian pyramid decomposition generates the best results.
The Laplacian Pyramid decomposition is a technique used in image processing to represent an image at multiple levels of resolution or detail. The idea is to decompose an image into a series of increasingly smoothed and down-sampled versions, called a Gaussian Pyramid, and then subtract the corresponding levels of the Gaussian Pyramid from the original image to obtain a set of Laplacian images. Each Laplacian image represents the residual or the high-frequency details of the image that were lost during the smoothing and down-sampling process.
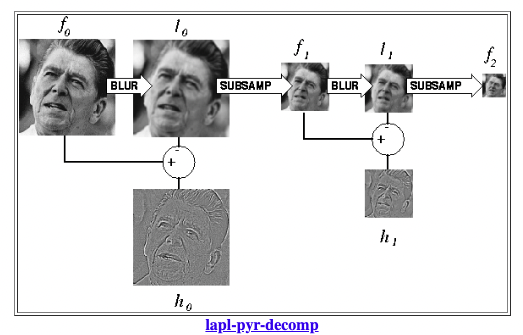
The Wang and Chang’s paper: A Multi-focus Image Fusion Method Based on Laplacian Pyramid introduces the method of using Laplacian Pyramid Decomposition to fuse images with different depth-of-focus. The method starts by decomposing each of the input images into a Laplacian Pyramid and then using the high-frequency details of each pyramid to create a weight map that indicates the focus level of each pixel. The weight maps are then used to combine the images into a single multi-focus image.
Using Focus Stacking
Inspired by the paper, I implemented focus stacking in Python. In addition to the paper, not only two images, but also multiple images can be fused together. In the latest version, the program also supports colored image.
# First clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/bznick98/Focus_Stacking.git
# and go into project directory
cd Focus_Stacking
# (optional) Create a Python virtual environment for better package management. You can use conda, virtualenv, etc.
# Install required packages: OpenCV, Matlplotlib
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run focus stacking program by:
python run.py PATH/TO/IMAGE/DIR/
# or specify images separately
python run.py PATH/TO/IMAGE1.jpg PATH/TO/IMAGE2.jpg ...
# For more argument detail, see:
python run.py -h
Rough Performance Evaluation
To evaluate the quality of final image, we can calculate the average gradient magnitude of pixel values in each image, which is an indicator of sharpness. This metric will represents focusness of the image, higher is better.
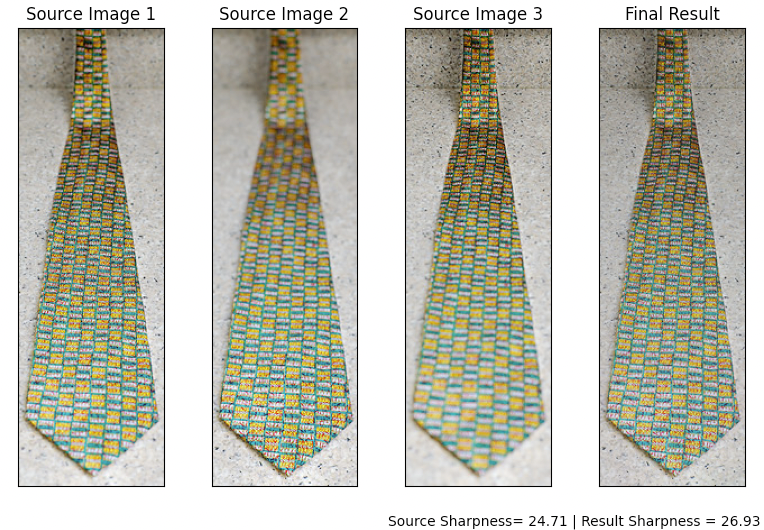
| Example 1 | Average Gradient Magnitude (Sharpness) |
|---|---|
| Average of Source Images | 24.71 |
| Final Result | 26.93 |

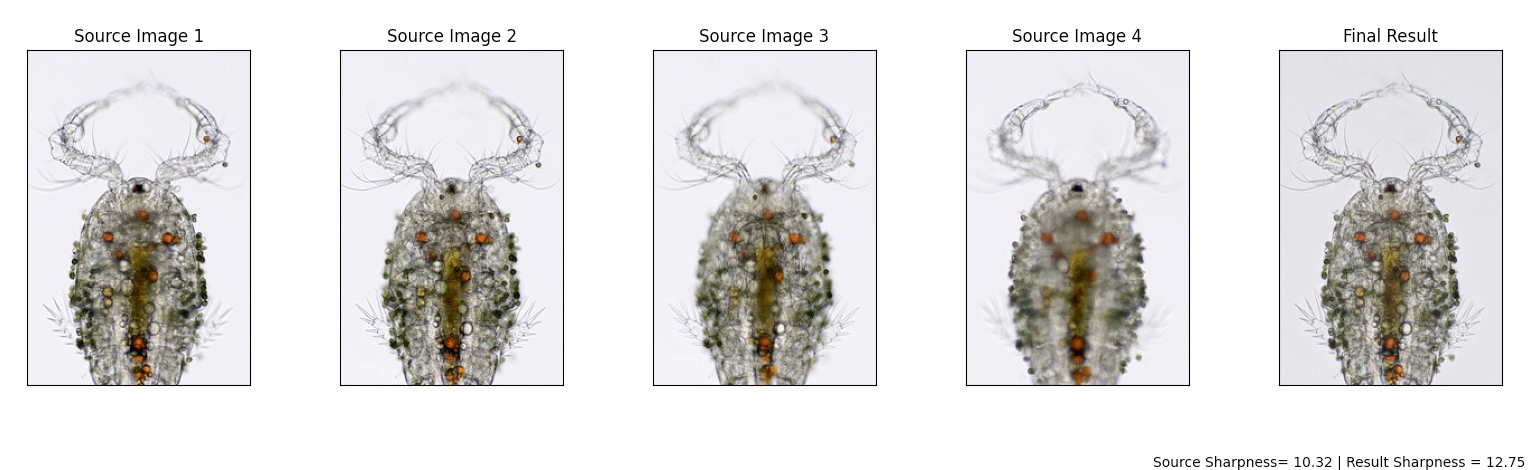
Examples below are taken from https://www.heliconsoft.com/helicon-focus-gallery/, where I screenshot several frames as the input images, the results produced are visually similar to the one produced by helicon-focus-gallery.
| Example 2 | Average Gradient Magnitude (Sharpness) |
|---|---|
| Average of Source Images | 10.32 |
| Final Result | 12.75 |

| Example 3 | Average Gradient Magnitude (Sharpness) |
|---|---|
| Average of Source Images | 5.47 |
| Final Result | 10.61 |

| Example 4 | Average Gradient Magnitude (Sharpness) |
|---|---|
| Average of Source Images | 9.24 |
| Final Result | 11.73 |

From this rough measurement we can see that the final result has the highest sharpness among all images, meaning it achieves the highest focusness. A future work is to come up with a better measurement of focusness and setup a testing set for measuring the performance of focus stacking algorithms.